建筑工人的健康、社交网络和社会资本对工作绩效的影响评估:以中国建筑工人为例
2019-01-09工学论文论文模板屋2296°c
A+ A-论文导读
摘要:多年来,建筑业一直被认为是事故、意外伤害和职业疾病高发的行业之一。这些针对建筑工人的风险会导致低绩效和社会问题。因此,建筑工人的福祉应该被高度关注以促进其工作绩效。同时,来源于建筑工人社交网络和社会资本方面的支持亦被认为是一种有效促进其身心健康和工作绩效的方法。本文基于广泛的文献综述,提出了一个健康、社交网络和社会资本视角下的促进建筑工人工作绩效的概念模型。本文在南京发放问卷来调查建筑工人的健康、社交网络、社会资本以及工作绩效情况。文章采用结构方程模型来测试建筑工人身心健康、社交网络、社会资本和工作绩效之间的三种假设关系。结果表明,建筑工人的身心健康对工作绩效的直接影响比社交网络和社会资本更加明显。除此之外,建筑工人的社会资本和社交网络会通过影响其身心健康来间接地影响工作绩效。基于上述分析,本文提出了提高建筑工人工作绩效的几点策略以及基于政府视角的几点建议。本文识别出的工作绩效影响因素和关系能够有效地促进建筑工人的工作绩效评估和健康管理工作。
关键词:结构方程模型;身心健康;社交网络;社会资本;工作效率;劳动生产率;
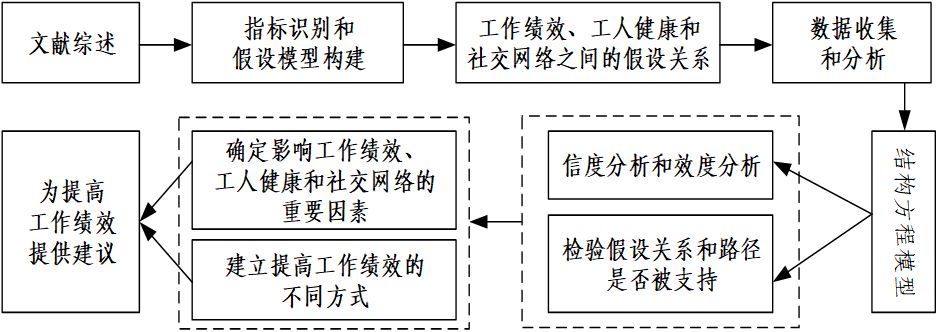
技术路线
研究假设
1、Hypothesis 1:P&M health has the positive influence on work efficiency and productivity.
假设1:身心健康对工作绩效有积极作用。
2、Hypothesis 2:The SNC has the positive influence on work efficiency and productivity.
假设2:社交网络和社会资本对工作绩效有积极作用。
3、Hypothesis 3:The SNC has the positive influence on P&M health.
假设3:社交网络和社会资本对身心健康有积极作用。
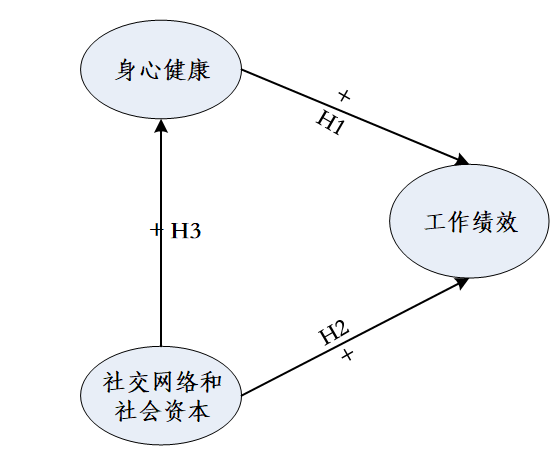
图 本文概念模型
论文结论
1、第一个假设(H1)是身心健康对工作绩效有正向影响。H1得到SEM (路径系数为0.67)结果的支持,这意味着工作绩效的提高应该依赖于建筑工人身心健康的改善。此外,良好的健康是一个建设项目成功的关键。
2、第二个假设(H2)是社交网络和社会资本的支持对工作绩效有正向影响。H2也得到SEM (路径系数为0.25)结果的支持,这意味着建筑项目的管理应该从政府和企业的角度为建筑工人提供更多的支持。由于现场临时工作的建筑工人的脆弱性和与用人单位关系的脆弱性,需要更多的政府监管、更有效的工作保护和更频繁的健康培训。
3、第三个假设(H3)是社交网络和社会资本对建筑工人的身心健康有正向影响。H3也得到了SEM (路径系数为0.91)结果的有力支持,这意味着社交网络和社会资本可以直接或间接影响健康。此外,职业健康培训对自我保护的影响被证明是显著正向的,这也支持了社交网络和社会资本对身心健康有正向影响。
研究建议
•比较三者之间的因素负荷关系,提高建筑工人工作绩效最重要、最直接的方法是促进建筑工人的身心健康。与社交网络和社会资本对工作绩效的直接影响相比,身心健康对工作绩效的直接影响更大。经常体检和合理的作息时间是提高身心健康和工作绩效的最佳途径。同时,加强自我保护意识、保持合理的工作时间、减少焦虑不安情绪的发生,也是提高建筑工人身心健康和工作绩效的有效途径。
•考虑到社交网络和社会资本对工作绩效率的直接影响,增加对建筑工人的社会支持也可以提高工作绩效。提高政府检查频率,可以加强政府的监督和支持,有利于建立健康的工作环境。从社交网络和社会资本的直接影响来看,加强企业提供的防护措施和职业健康培训是提高工作绩效的有效途径。
•此外,社交网络和社会资本通过影响身心健康,可以间接影响工作绩效。来自社交网络和社会资本的支持对身心健康大有裨益。社会支持可以提高工作幸福感以减少心理压力(如焦虑和不安情绪)。社会支持也可以促进自我保护意识的提高。此外,来自企业的社会支持可以提供体检,帮助工人了解自己的健康信息,以增强自我保护意识。
原文摘要
The construction industry has been recognized, for many years, as among those having a high likelihood of accidents, injuries and occupational illnesses. Such risks of construction workers can lead to low productivity and social problems. As a result, construction workers’ well-being should be highly addressed to improve construction workers’ efficiency and productivity. Meanwhile, the social support from a social network and capital (SNC) of construction workers has been considered as an effective approach to promote construction workers’ physical and mental health (P&M health), as well as their work efficiency and productivity. Based on a comprehensive literature review, a conceptual model, which aims to improve construction workers’ efficiency and productivity from the perspective of health and SNC, was proposed. A questionnaire survey was conducted to investigate the construction workers’ health, SNC and work efficiency and productivity in Nanjing, China. A structural equation model (SEM) was employed to test the three hypothetical relationships among construction workers’ P&M health, SNC and work efficiency and productivity. The results indicated that the direct impacts from construction workers’ P&M health on work efficiency and productivity were more significant than that from the SNC. In addition, the construction workers’ social capital and the network can indirectly influence the work efficiency and productivity by affecting the construction workers’ P&M health. Therefore, strategies for enhancing construction workers’ efficiency and productivity were proposed. Furthermore, many useable suggestions can be drawn from the research findings from the perspective of a government. The identified indicators and relationships would contribute to the construction work efficiency and productivity assessment and health management from the perspective of the construction workers.

